In the fast-evolving world of blockchain technology, scalability remains a major challenge for developers building decentralized applications (dApps). As Ethereum’s ecosystem grows, solutions like Avalanche Subnets and Polygon Supernets have emerged to help create customized, high-performance blockchains. Moreover, these tools allow projects to launch their own “app chains” – dedicated networks tailored to specific needs – without the congestion and high fees of main chains.
If you’re new to blockchain, think of these as specialized highways branching off from a busy freeway. Essentially, they let traffic (transactions) flow smoothly for particular vehicles (apps), improving speed and efficiency. In this article, we’ll break down Avalanche Subnets vs Polygon Supernets in simple terms, highlighting their features, similarities, differences, and real-world uses. Whether you’re a beginner exploring crypto or a developer considering scalability options, this guide will help you understand these powerful tools.
By the end, you’ll grasp how these networks compare in terms of performance, security, and customization – all based on verified facts from reliable sources.
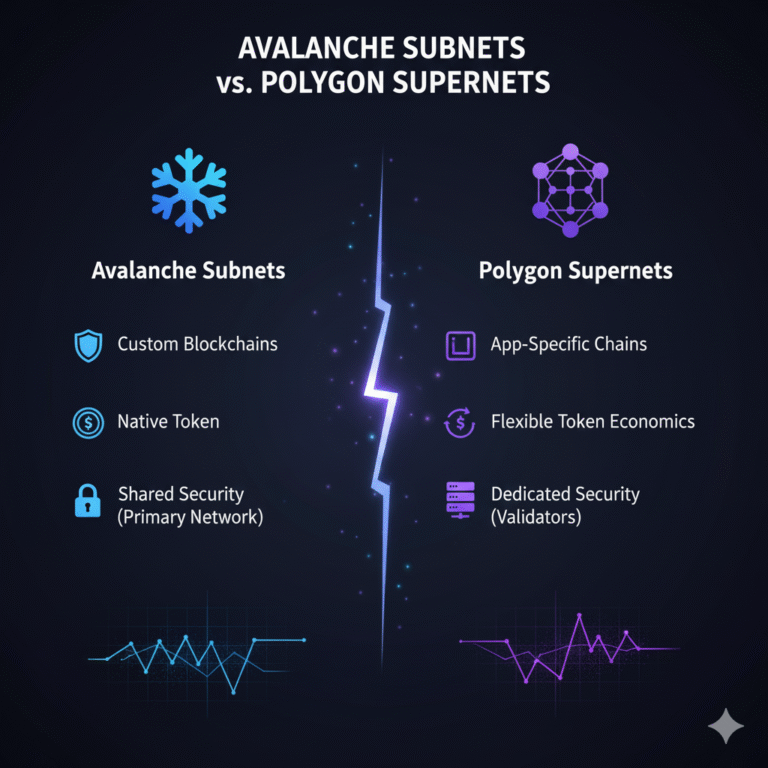
What Are Avalanche Subnets?
Avalanche Subnets, also known historically as custom L1s within the Avalanche ecosystem, are dynamic groups of validators that work together to secure and process transactions on one or more custom blockchains. Specifically, they build on Avalanche’s architecture of three primary chains: the X-Chain (assets), P-Chain (validators/subnets), and C-Chain (EVM smart contracts). Learn more at Avax.network.
Important Clarification: Since the Etna upgrade, Avalanche now formally distinguishes between “legacy Subnets” and “Avalanche L1s.” Legacy Subnets still require validators to also validate the Primary Network; however, newer Avalanche L1s pay a continuous fee and do not require Primary Network validation. This article uses “Subnets” in the broad sense but notes this change where relevant. For a deeper dive into this evolution, check out our detailed guide on Avalanche L1s (formerly Subnets): Modular DeFi in Action. Additionally, you can find technical details at the Avalanche Developer Hub.
At their core, Subnets allow developers to create sovereign networks with their own rules. For example, you can set custom gas tokens (instead of using AVAX), implement access controls like KYC requirements, or design unique fee structures. Furthermore, each Subnet operates independently but can connect to the broader Avalanche network.
How Avalanche Subnets Work
To join a legacy Subnet as a validator, you must stake at least 2,000 AVAX and validate the Primary Network (X, P, C chains) in addition to the Subnet. Consequently, this ensures security but adds a layer of commitment. For new Avalanche L1s, this Primary Network requirement no longer applies, as noted above. Detailed staking information is available at Avalanche Support.
Subnets use the Snowman family of protocols with Avalanche consensus (proof-of-stake based), which provides probabilistic finality with very low reversal probability when parameters are set appropriately. In other words, the system achieves consensus quickly and reliably. Find architectural documentation at the Avalanche Builder Hub.
Beginners can picture this like a team of guards (validators) agreeing on what’s happening in a secure room (the blockchain). The process is highly configurable: you can choose EVM compatibility for easy smart contract deployment or build custom virtual machines (VMs) in other languages.
Benefits for Beginners
Scalability: Avalanche markets throughput of approximately 4,500+ TPS for its platform; however, actual realized TPS depends on the VM and network configuration of each chain/Subnet. Performance metrics are detailed on Avax.network.
Customization: You can tailor tokenomics, gas tokens, validator requirements, and even your own VM according to your project’s specific needs. This flexibility makes Subnets particularly attractive for specialized use cases.
Security: The system leverages Avalanche’s validator set design; notably, it implements no slashing on the default/primary network (poor performance forfeits rewards rather than stake). As a result, this approach reduces penalties while maintaining network integrity.
For instance, if you’re building a gaming dApp, a Subnet could handle heavy in-game activity without slowing the main network. This separation of concerns ensures optimal performance across all applications.
What Are Polygon Supernets?
Polygon Supernets are application-specific blockchain networks built using Polygon Edge, a modular framework for creating Ethereum-compatible chains. Notably, developers introduced Supernets in April 2022 alongside a $100M ecosystem fund to accelerate adoption. Official information is available at Polygon.technology.
Supernets focus on interconnectivity, allowing seamless communication with Ethereum and other Polygon networks. They come in different flavors: sovereign chains (run by your own validators) and shared security chains (validated by professional operators with POL/MATIC stake). Furthermore, Polygon also offers ZK L2s via Polygon CDK; earlier Supernet materials referenced L2 options as “under development.” To understand how Polygon compares to other major blockchains, read our comprehensive comparison: Ethereum vs Solana vs Polygon: Which Blockchain Wins for DeFi?. Additionally, explore the technical documentation at Polygon Docs.
How Polygon Supernets Work
Supernets use IBFT (PoA/PoS variants), which provides deterministic finality – once a block is finalized, it does not reorganize. In shared security mode, Polygon materials describe validators staking ≥20,000 MATIC (now POL); meanwhile, sovereign Supernets can run with a small validator set for testing. Validator counts on IBFT networks are configurable; however, Polygon’s PoS network itself caps validators at 100, and IBFT performance tends to favor relatively small validator sets. Technical specifications are documented at Polygon Edge Documentation.
Developers typically configure block time on Polygon Edge-based networks around 2 seconds by default (and they can adjust it). Implementation details can be found on GitHub.
Imagine assembling Lego blocks: you pick modules for consensus, data storage, and networking to build a chain that fits your app. Similarly, EVM compatibility means you can deploy Solidity contracts using familiar tools like MetaMask or Hardhat.
Benefits for Beginners
Ease of Use: Certified partners and tooling reduce setup burden, making deployment accessible even for teams with limited blockchain infrastructure experience. Consequently, developers can launch faster with less technical overhead.
Interoperability: Bridges and native Ethereum tooling enable seamless integration with the broader Ethereum ecosystem. For more on cross-chain scalability solutions, see our guide on Understanding ZK Rollups: A Beginner’s Guide to Ethereum’s Scaling Solution.
Cost Efficiency: Supernets offer low fees and fast finality; however, actual TPS depends on configuration and workload rather than a single fixed number. This flexibility allows projects to optimize for their specific requirements.
Real-World Application: Uttarakhand State (India) piloted medical-equipment tracking using a network built with Polygon Edge (the tech behind Supernets). Read about this implementation at Business Standard.
Key Similarities Between Avalanche Subnets and Polygon Supernets
Both solutions enable “app chains” – dedicated blockchains for specific dApps – reducing congestion on shared main chains while offering several common features. In fact, they represent parallel approaches to the same fundamental challenge.
Customization Focus: Both platforms allow you to tune gas tokens, tokenomics, and network rules to meet specific project requirements. This flexibility empowers developers to create truly custom blockchain environments.
EVM Compatibility: Both support Ethereum tooling, making migration and development straightforward for Solidity developers. As a result, teams can leverage existing skills and infrastructure.
Stake-Backed Security: Validators stake native tokens or network-specific stake for security (AVAX/Elastic-Subnet tokens on Avalanche; POL/MATIC-backed professional validators or sovereign sets on Polygon). Therefore, both systems align incentives through economic mechanisms.
Real-World Adoption: Examples include DeFi Kingdoms (DFK Chain) and Crabada on Avalanche Subnets, and SX Network and public-sector pilots on the Polygon Edge/Supernets stack. Documentation for these projects can be found at DeFi Kingdoms Docs and related blockchain analytics platforms like The Tie.
Blockchain-as-a-Service: Tooling abstracts complex setup, making custom blockchain deployment more accessible to projects without deep infrastructure expertise. Consequently, this democratizes access to advanced blockchain technology.
Key Differences: Avalanche Subnets vs Polygon Supernets
Consensus & Finality
Subnets: Avalanche implements consensus (Snowman family) with probabilistic finality (extremely fast, extremely low reorg probability). In practice, this means transactions confirm rapidly while maintaining high security. Technical details at Avalanche Builder Hub.
Supernets: By contrast, IBFT provides deterministic finality, ensuring that once blocks are confirmed, they cannot be reorganized. Specifications at Polygon Edge Documentation.
Validator Model & Requirements
Legacy Subnets: Validators must also validate the Primary Network and stake ≥2,000 AVAX; however, new Avalanche L1s remove that Primary Network requirement (they pay a continuous fee instead). Details at Avalanche Support.
Supernets: Developers can configure validator counts in IBFT, but practice favors smaller sets; Polygon PoS caps validators at 100, which people often cite as an upper bound reference for IBFT-style networks. Additionally, shared security Supernets describe ≥20,000 MATIC/POL per validator. More information at Polygon.technology.
Performance Framing
Avalanche markets approximately 4,500 TPS capability; nevertheless, actual throughput per Subnet/L1 depends on VM/configuration. Fixed “per-Subnet TPS” figures are marketing approximations, not guarantees. For a detailed comparison of blockchain performance metrics, see our analysis: Ethereum vs Solana vs Polygon vs TON: Chain Metrics Compared.
For Supernets, TPS depends on block size/time and workload; therefore, quoting a single “1,500 TPS” figure is not consistently documented in Polygon’s official sources, so treat it as configuration-dependent rather than a hard ceiling. Developers commonly set block time around 2 seconds. Industry analysis available on Medium and Cointelegraph.
Slashing & Incentives
Avalanche (default): The network implements no slashing; instead, misbehavior or downtime forfeits rewards rather than stake. Furthermore, Subnets/L1s can design their own economics according to project needs.
Polygon/IBFT ecosystems: By contrast, projects often adopt slashing or stake-based deterrence aligned with Ethereum-style practices on networks using staking markets.
Interoperability Roadmaps
Both use bridges for cross-chain communication; however, Polygon’s broader stack emphasizes ZK-based L2s via Polygon CDK for cross-ecosystem connectivity (separate from Supernets themselves). For an in-depth exploration of ZK technology, read our complete guide: ZK Rollups Complete Guide 2025: Zero-Knowledge Layer 2 Solutions Explained. Comprehensive information at Polygon Docs.
In short, Subnets/L1s favor raw configurability (including tokenless/private chains) and extremely fast probabilistic finality; meanwhile, Supernets emphasize Ethereum synergy and managed operations with deterministic finality.
Use Cases and Real-World Examples
Avalanche Subnets
DeFi Kingdoms (DFK Chain) uses JEWEL as gas with a documented gas-fee split (50% burned / 25% validators / 25% quest fund); similarly, Crabada’s Swimmer Network recorded average gas fees roughly 1/120th of those on C-Chain, improving user experience. Moreover, enterprises like Deloitte have used Avalanche tech for disaster-relief claims platforms. Case studies available on Medium and DeFi Kingdoms Docs.
Polygon Supernets / Edge
SX Network was an early standalone chain built with Polygon Edge (the foundation for Supernets). Additionally, public-sector pilots like Uttarakhand’s asset-tracking (RFID) leveraged Polygon Edge as well. Project information at Polygon.technology.
These examples show both approaches powering gaming, DeFi, and enterprise/government solutions across diverse industries. Consequently, they demonstrate the versatility of app-chain architecture.
Pros and Cons of Each
Avalanche Subnets / L1s – Pros
- Developers enjoy high configurability and performance potential (VM choice, custom gas tokens)
- The platform offers flexibility for private/enterprise use; notably, it implements no slashing by default on the primary network
- Teams can create fully sovereign blockchains with custom consensus mechanisms
Avalanche Subnets / L1s – Cons
- Legacy Subnets require Primary Network validation (2,000 AVAX), which adds overhead; however, new Avalanche L1s ease this but add a continuous fee
- Probabilistic (not deterministic) finality may be a conceptual hurdle for some stakeholders (though developers can tune reorg probability extremely low)
Polygon Supernets – Pros
- The platform provides deterministic finality (IBFT) and tight Ethereum tooling compatibility
- Partner support and deployment tooling lower operational burden
- Projects benefit from strong ecosystem connections to Ethereum and established DeFi protocols
Polygon Supernets – Cons
- IBFT networks perform best with relatively small validator sets; some view Polygon PoS’s 100-validator cap (often used as a practical reference point) as a decentralization limit
- Throughput is configuration-dependent; therefore, quoting fixed TPS numbers (e.g., “1,500 TPS”) without context is misleading
- Bridge Risk (both): Bridging remains a systemic risk; while architecture and validator decentralization help, they don’t eliminate it entirely
Which One Should You Choose?
If you prioritize raw configurability (custom VMs, tokenless/private chains) and ultra-fast probabilistic finality for high-volume apps (e.g., GameFi), then Avalanche Subnets/L1s are compelling. On the other hand, if you want deterministic finality, strong Ethereum tooling, and an easier, partner-supported path, Polygon Supernets fit well.
Consider your team’s expertise: Subnets/L1s suit those comfortable with deeper chain customization; meanwhile, Supernets appeal to Solidity-native teams. Additionally, always evaluate validator set design and operational trust assumptions before making a decision. Understanding these factors will help you choose the right platform for your specific needs.
Conclusion: The Future of Scalable Blockchains
Avalanche Subnets/L1s and Polygon Supernets both represent the shift toward multi-chain worlds, where apps get their own optimized networks. By enabling customization without prohibitive complexity, they empower beginners and experts alike to build scalable dApps. Furthermore, this evolution addresses many of the scalability challenges that have historically limited blockchain adoption.
For the latest specifics (e.g., Avalanche’s Etna changes, Polygon’s CDK rollouts), always consult the official documentation at Avalanche Developers and Polygon Docs – the space moves fast, and staying informed is crucial for success. Additionally, explore our related guides on blockchain comparisons and scaling solutions to deepen your understanding of this rapidly evolving ecosystem.
Key Resources: