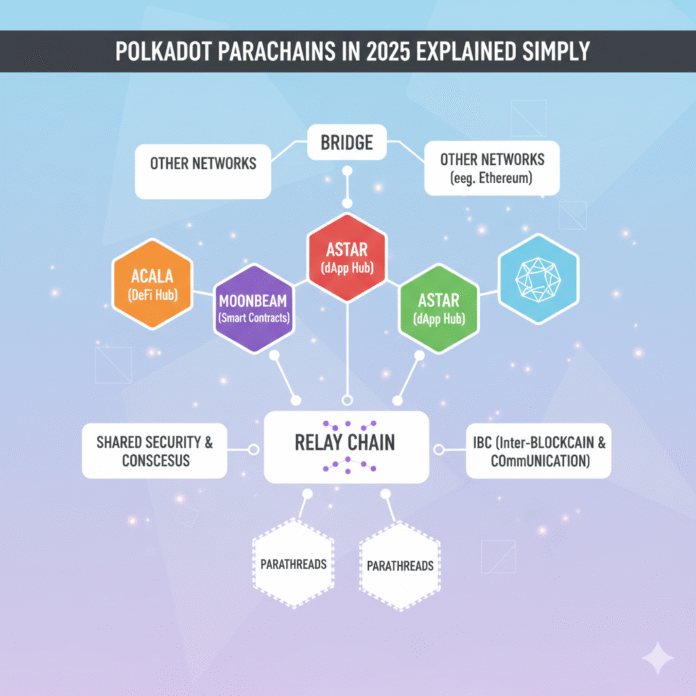
In the fast-moving world of blockchain, Polkadot stands out for one big reason: it connects multiple blockchains into a single interoperable ecosystem. At the center of this design are parachains — specialized blockchains that bring scalability, shared security, and cross-chain communication to life.
Think of Polkadot as a main highway (the Relay Chain) with many side roads (parachains) that plug in and send traffic between one another. Consequently, this setup prevents congestion and allows blockchains to cooperate instead of competing. By 2025, Polkadot’s parachain system has matured dramatically thanks to upgrades such as Agile Coretime and Polkadot 2.0, which redefine how resources are allocated and networks scale.
This guide breaks everything down in plain language — what parachains are, how they work, what changed in 2025, and why these updates matter for developers, users, and investors exploring Web3.
What Are Polkadot Parachains?
Parachains are independent, application-specific blockchains that run in parallel to the Polkadot Relay Chain. Unlike standalone networks that must secure themselves, parachains share the Relay Chain’s validator set and consensus, thereby saving massive time and cost according to the official Polkadot Wiki.
Key Characteristics
Shared Security – Every parachain inherits Polkadot’s proof-of-stake security. As a result, smaller projects don’t need their own validator network. This shared security model is crucial for understanding how to protect your crypto assets across different blockchain ecosystems.
Parallel Processing – Multiple parachains can process transactions simultaneously, which drastically improves throughput. This approach differs significantly from how other networks handle scalability, as explored in our comparison of Cosmos vs Polkadot’s different paths to interoperability.
Interoperability via XCM – The Cross-Consensus Message Format (XCM) lets parachains exchange data or assets natively as detailed in Polkadot’s XCM documentation.
Custom Logic – Each parachain can have unique governance, tokens, and fee models, unlike rigid smart-contract chains.
Simplified Workflow
First, collators gather transactions on a parachain and produce block candidates. Subsequently, they include Proof-of-Validity (PoV) data for Relay Chain validators.
Next, validators verify these PoV proofs using WebAssembly executables, thereby ensuring that the new state is valid.
Once verified, the Relay Chain merges all parachain states into a single global state.
The result: parallel execution, shared security, and smooth communication — a combination that few other ecosystems achieve.
From Slot Auctions to Agile Coretime
Before 2025, launching a parachain required slot auctions. Projects bid large amounts of DOT to lease a slot for up to 96 weeks, often raising community support through crowdloans.
However, in 2025, this system was replaced by Agile Coretime, a flexible resource-rental model described by Parity Technologies and the Polkadot community.
How Agile Coretime Works
Coretime = Computational Access. Instead of a fixed slot, projects buy coretime — a slice of execution capacity on the Relay Chain.
Two Modes:
- Bulk Purchase – designed for stable, long-term projects needing consistent throughput
- On-Demand Purchase – ideal for variable workloads; pay per block when needed
Dynamic Pricing: Furthermore, coretime prices adjust monthly based on supply and demand as explained in the Polkadot Fellowship RFC.
Deflationary Mechanics: Additionally, purchased DOT may be burned (permanently removed from circulation), tightening token supply. For those looking to acquire DOT tokens, checking out top crypto exchanges for beginners can help you get started safely.
Coretime Marketplaces: Meanwhile, platforms such as RegionX and Lastic are being built to let developers buy and manage coretime packages.
Why It Matters
Notably, Agile Coretime lowers the entry barrier for smaller teams, eliminates waste from idle slots, and enables a pay-as-you-go economy. Moreover, it’s one of the cornerstones of Polkadot 2.0 — the new, more dynamic version of the network.
The Polkadot 2.0 Upgrade — Core Components
Polkadot 2.0 isn’t a single feature; rather, it’s a series of upgrades that redefine performance and scalability as documented in Polkadot’s official documentation.
| Component | What It Does | 2025 Status |
|---|---|---|
| Asynchronous Backing | Validates blocks off the main path, improving block times | Rolling out in 2025 |
| Elastic Scaling | Lets a parachain use multiple cores at once (multi-core execution) | Gradual rollout; early testing stages |
| JAM Protocol (Join-Accumulate Machine) | Redesigns Polkadot’s computation engine for higher efficiency | Concept approved, partial implementation |
| Asset Hub + EVM Support | Enables native asset transfers and Solidity-based smart contracts | Active improvement in 2025 |
Together, these innovations push Polkadot toward becoming a self-scaling multichain operating system — a foundation for everything from DeFi and DePIN to gaming. While Solana and TON are gaining traction with different approaches, Polkadot’s unique architecture offers distinct advantages for builders seeking interoperability. Similar scaling philosophies can be seen in Optimism’s Superchain approach, though with fundamentally different technical implementations.
Verified Metrics: Polkadot in 2025
Here are publicly verified figures from Messari’s Q1 2025 report and Polkadot community reports:
- Total Transactions (Q1 2025): 137.1 million (-36.9% QoQ, +76.3% YoY)
- Active Addresses: approximately 530 thousand per month, representing a decline from 610 thousand in late 2024
- Treasury Holdings: approximately 30.9 million DOT (roughly $124 million), with 92% of assets held in DOT
- DOT Token Cap: Hard-capped at 2.1 billion tokens — approved by on-chain governance
- DeFi Deployments: approximately 15% of treasury assets placed across DeFi parachains such as Hydration, Centrifuge, and Bifrost
Although overall transactions dipped during the transition to new mechanisms, the ecosystem remains robust and diverse.
Notable Parachains and Use Cases
The Polkadot ecosystem in 2025 hosts a wide mix of active parachains accessible through the Polkadot parachain directory:
Moonbeam – An EVM-compatible chain attracting Ethereum developers (moonbeam.network)
Peaq – Focused on DePIN (Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Networks), notably reporting +84% transaction growth QoQ (peaq.network)
Mythos – A game-oriented parachain driving millions of transactions monthly (mythos.foundation)
Acala, Parallel, Centrifuge – Leading DeFi and real-world-asset (RWA) platforms. For those interested in stablecoin infrastructure, understanding how stablecoins work on Ethereum provides useful context for comparing DeFi ecosystems across different chains.
Phala Network – Specialized in confidential computing via Trusted Execution Environments (TEE) (phala.network)
These projects illustrate how Polkadot has evolved from an interoperability concept into a diverse ecosystem spanning finance, gaming, and infrastructure.
Advantages and Challenges in 2025
Main Advantages
Lower Barrier to Entry – Teams no longer need multi-million-DOT auction bids. Instead, coretime can be rented cheaply.
Cost Efficiency – Projects pay only for the computation they actually use, which significantly reduces operational expenses.
Deflationary Tokenomics – Burning DOT via coretime purchases reduces supply and may support long-term value accordingly.
Ecosystem Diversity – Easier onboarding brings more niche chains — gaming, DePIN, privacy, AI, IoT. Consequently, the network becomes more versatile.
Better Cross-Chain UX – Asset Hub and enhanced XCM enable smooth transfers and composability, thereby improving user experience.
Ongoing Challenges
Transition Complexity – Coretime marketplaces and elastic scaling are still being rolled out, which presents temporary hurdles.
Resource Competition – When demand spikes, projects may compete for limited coretime supply. Therefore, strategic planning becomes essential.
Management Overhead – Developers must plan budgets and monitor real-time pricing, adding operational complexity.
Partial Feature Deployment – JAM and multi-core execution remain in testing, meaning full capabilities aren’t yet available.
Ecosystem Noise – Some network activity still comes from staking and governance, not user apps — a sign of a maturing but still shifting ecosystem.
Example: Launching a Gaming Parachain in 2025
Let’s imagine a studio building a Web3 game:
Old Way: Bid in slot auctions → lock DOT for 96 weeks → huge cost
Now: Instead, buy coretime to launch quickly → scale up during events → scale down after
If successful: Subsequently, adopt elastic scaling to run on multiple cores
Interoperability: Furthermore, game assets (NFTs, tokens) can move via XCM or Asset Hub to other chains. This is particularly relevant as NFT utility continues to evolve across different blockchain ecosystems.
Economics: Additionally, part of the DOT paid for coretime is burned, thereby reducing supply
The result — faster launch, lower costs, and seamless player experience secured by Polkadot’s Relay Chain.
The Bigger Picture — Polkadot’s Position in 2025
Polkadot’s upgrades aim to make it the most flexible multi-chain platform for Web3 builders.
For Developers: Build independent blockchains without running validator networks, thus reducing infrastructure costs.
For Users: Enjoy cheaper, faster, interoperable apps that seamlessly communicate across chains. As with any blockchain interaction, following essential security rules remains critical regardless of which ecosystem you’re using.
For Investors: DOT has clearer tokenomics and utility (burn + cap), which enhances long-term value proposition.
For Ecosystem Growth: Moreover, more on-chain DAOs, grants, and events are funding innovation. Notably, the 2025 Builder Party offered $40,000 in rewards for new projects.
These changes position Polkadot as a serious competitor to other scalable smart-contract platforms while staying true to its original goal — a secure, interconnected “internet of blockchains.”
Outlook for 2026 and Beyond
The coming year will likely bring several exciting developments:
First, we can expect full coretime marketplaces with secondary trading, allowing more flexible resource allocation.
Additionally, broader elastic scaling support for multi-core execution will significantly increase performance. As Layer 2 solutions continue to evolve across the industry — like StarkNet’s 2025 roadmap demonstrates — Polkadot’s approach offers a compelling alternative with its shared security model.
The network will also see JAM protocol rollouts that further increase throughput and efficiency across the network.
Finally, enhanced EVM and WASM bridging will make Polkadot attractive for both Ethereum and Substrate developers.
Polkadot 2.0 is not just an upgrade — rather, it’s a re-architecture of how blockchains share resources and scale. If delivered as planned, it could set a new standard for modular, interconnected networks.
Final Takeaway
By 2025, Polkadot parachains have evolved from an experimental concept into a mature, scalable framework for Web3. With Agile Coretime, shared security, and upcoming JAM and Elastic Scaling features, Polkadot is shaping the next generation of blockchain infrastructure — modular, efficient, and interconnected.
If you’re new to Web3 and looking for a network that combines technical depth with real-world usability, Polkadot in 2025 is a case study in how blockchain can grow up without giving up its decentralized soul.
Related Resources
- Official Polkadot Documentation
- Polkadot GitHub
- Substrate Developer Hub
- Web3 Foundation
- Polkadot Forum
Disclaimer: This article presents information about blockchain technology and cryptocurrency for educational purposes. Features mentioned as “in development” such as JAM Protocol and full Elastic Scaling implementation are subject to change. Always conduct your own research before making investment decisions.