Dynamic NFTs, also known as dNFTs, are revolutionizing the NFT space by bringing live, evolving digital assets to blockchain. If you’ve ever wondered how dynamic NFTs work, this guide breaks it down simply.
Imagine owning a digital collectible that changes appearance, unlocks perks, or gains value based on real-world events—like a sports score, weather data, or your gaming progress. That’s the magic of dynamic NFTs.
In this comprehensive article, we’ll explain dynamic NFTs for beginners, cover how they work step-by-step, share dynamic NFT examples, and explore their future. Backed by verified sources like Chainlink and Ethereum Improvement Proposals, this is your ultimate guide to dynamic NFTs in 2025.
What Are NFTs? A Quick Refresher
Before diving into dynamic NFTs, let’s recap NFTs (Non-Fungible Tokens).
NFTs are unique digital tokens on a blockchain, like Ethereum, proving ownership of art, music, videos, or virtual items. They use standards like ERC-721 (one-of-a-kind) or ERC-1155 (can represent both non-fungible and semi-fungible items in one contract).
Static NFTs—the most common type—are immutable. Once minted, their metadata (image, traits, description) stays fixed. Stored on IPFS or centralized servers, they appear the same forever. Despite debates about whether NFTs on Ethereum are still relevant or already dead, the technology continues to evolve with dynamic capabilities.
Enter dynamic NFTs: These evolve automatically. Their metadata updates based on triggers, making them “living” assets.
Definition: A dNFT is an NFT whose smart contract logic enables automatic metadata changes based on external conditions (time, events, data). Source: Chainlink documentation
Static NFTs vs. Dynamic NFTs: Key Differences
| Feature | Static NFTs | Dynamic NFTs (dNFTs) |
|---|---|---|
| Changeability | Fixed forever | Updates over time |
| Metadata | Immutable URI | Mutable or regenerated |
| Triggers | None | On-chain events, off-chain data |
| Use Cases | Art collectibles | Games, RWAs, loyalty programs |
| Cost | Low minting | Higher for updates (gas fees) |
Static NFTs are like photographs—beautiful but unchanging. Dynamic NFTs are like videos—they play out over time.
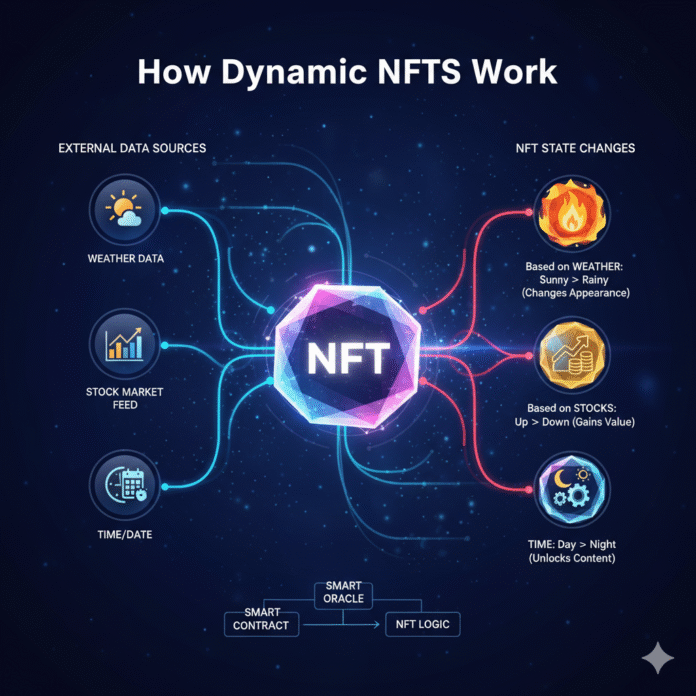
How Do Dynamic NFTs Work? Step-by-Step Breakdown
Dynamic NFTs rely on smart contracts with built-in logic to fetch data and update metadata. Here’s how dynamic NFTs work:
1. Minting the Base NFT
Deploy a smart contract (ERC-721/1155) on Ethereum, Solana, or other blockchain platforms. Mint the NFT with an initial URI (Uniform Resource Identifier) pointing to JSON metadata stored on IPFS or similar decentralized storage.
Example JSON metadata structure:
json
{
"name": "Evolving Ghost #1",
"image": "ipfs://QmInitialImage",
"attributes": [{"trait": "Level", "value": 1}]
}2. Triggers for Change
On-chain triggers: Time-based conditions (e.g., after 30 days), transaction events, or user actions recorded directly on the blockchain.
Off-chain triggers: Real-world data fetched via oracles like Chainlink, which can retrieve stock prices, weather conditions, or sports scores.
When triggered, the smart contract executes the programmed logic. Understanding how gas optimization is revolutionizing DeFi fees is crucial, as update transactions can be costly without proper optimization strategies.
3. Updating Metadata
The smart contract calls updateURI() or similar functions to point to new metadata. Updated JSON files and images are uploaded to decentralized storage solutions like IPFS, Arweave, or Irys.
Important note: On Irys, mutability uses a tag named Root-TX that links new uploads to the original transaction; the canonical URL then resolves to the latest version.
Marketplaces like OpenSea can refresh to show changes. Many indexers now watch ERC-4906 metadata-update events for automated refreshes.
4. Verification and Display
Blockchains ensure immutable ownership records. Owners see evolved traits in wallets and marketplaces once metadata refresh propagates. On OpenSea, metadata refresh can be triggered via UI or API, and platforms increasingly support ERC-4906 events for automatic updates.
Simple analogy: Like a Pokémon that levels up—your NFT “grows” without losing its uniqueness.
On-Chain vs. Off-Chain Dynamic NFTs
Fully On-Chain
Pros: Maximally decentralized; can store SVG or image logic directly in the contract.
Cons: Higher gas costs and limited data size. Tutorials commonly show fully on-chain SVG dNFTs updated by Chainlink Automation.
Off-Chain Metadata (Most Common)
Pros: Cost-effective, scalable, supports rich media.
Cons: Some centralization risk depending on storage and indexing solutions.
Oracles like Chainlink are used to bridge real-world data securely to smart contracts. Alternative blockchain ecosystems like those discussed in BNB Smart Chain in 2025: Still a Powerhouse or a Centralized Ghost offer different trade-offs for deploying dynamic NFTs with varying levels of decentralization and cost efficiency.
Key Technologies Powering Dynamic NFTs
Token Standards: ERC-721 (unique tokens), ERC-1155 (multi-token contracts, including semi-fungible assets).
Oracles: Chainlink for reliable off-chain data feeds and Verifiable Random Function (VRF) for provable randomness.
Automation: Chainlink Automation (formerly Keepers) for scheduled or condition-based updates—so dNFTs can evolve without manual intervention.
Storage: IPFS, Arweave, and Irys for permanent or mutable metadata storage (via Root-TX tagging).
Related and Emerging Extensions
ERC-4906 (metadata update events) is widely referenced by marketplaces to detect and display updates automatically.
ERC-6551 (token-bound accounts) lets NFTs own assets and interact with applications, often paired with dNFT logic for advanced functionality.
Note: “ERC-7110 / ERC-721D (dynamic ownership)” is a community proposal discussed on Fellowship of Ethereum Magicians, not an adopted Ethereum standard; treat it as experimental.
Pro Tip: Use Chainlink Automation for automatic updates—no manual intervention required.
Real-World Dynamic NFT Examples
Aavegotchi: Uses Chainlink VRF to mint provably random traits and powers dynamic, evolving gameplay mechanics known as “rarity farming.” Source: Chainlink
Moonbirds: Features “Nesting” (locking) that accrues holder perks and status over time; it’s a hold-to-earn mechanic rather than guaranteed art changes. Source: OKX Wallet
Async Art: Programmable art platform where owners can change layers or pieces that evolve with time and external inputs. Source: Referenced in investment documentation
Gaming items: In many blockchain games, NFTs representing characters or items level up or change attributes based on player actions or oracle-fed events. Source: NDLabs
Real-World Assets (RWAs): Projects exploring tokenized real-world assets use dynamic metadata to reflect changing states (e.g., status, yields, or conditions) via oracle feeds. Modular blockchain solutions like Avalanche L1s (formerly Subnets) demonstrating modular DeFi in action provide scalable infrastructure for such complex dNFT implementations. Source: Chainlink
Benefits and Use Cases of Dynamic NFTs
Increased Utility: Earn yields, access exclusive events, or evolve rarity levels over time.
User Engagement: Gamification mechanics boost long-term retention and community involvement.
Real-World Bridge: Connects blockchain assets to real-world assets, digital identity, and loyalty programs.
Primary Use Cases
Gaming: Evolving avatars and items that grow with player progress, creating deeper engagement and real ownership of in-game assets. Source: NDLabs
Music and Ticketing: Event tickets or passes that unlock post-event perks, verified rewards, or exclusive content. The concept of NFT as access pass revolutionizing access beyond digital art demonstrates how dynamic NFTs can transform event management, membership systems, and exclusive community access models. Source: OpenSea Developer Documentation
DeFi: Yield-bearing NFTs or position tokens whose metadata updates with performance metrics, providing visual representations of financial positions. Source: Cube Exchange
Challenges and the Future of Dynamic NFTs
Current Challenges
Gas Fees: Metadata updates cost ETH on mainnet (though Layer-2 solutions significantly reduce costs). Implementing proper gas optimization techniques that are revolutionizing DeFi fees can make dynamic NFT updates more affordable for projects and users alike.
Oracle Risks: Data accuracy and uptime must be carefully managed to ensure reliable updates and prevent manipulation.
Adoption: Marketplaces and indexers need to detect and display changes properly. ERC-4906 helps standardize this process across platforms.
2025 Outlook
Layer-2 scaling solutions like Base and Optimism are lowering transaction costs dramatically, making frequent metadata updates economically viable. Standards like ERC-4906 and ERC-6551 are improving user experience and functionality. AI-driven smart contract logic and expanding real-world asset tokenization are opening new use cases for dynamic NFTs.
Cross-chain implementations on platforms like Avalanche L1s enabling modular DeFi and alternative chains such as BNB Smart Chain offer developers more options for deploying cost-effective dynamic NFT projects with different security and decentralization trade-offs.
Conclusion: Why Dynamic NFTs Matter
Dynamic NFTs transform collectibles into assets that live and breathe with the world. How do dynamic NFTs work? Through smart contracts, oracles, and mutable metadata—simple yet powerful technology that bridges digital and physical realities.
From serving as NFTs functioning as access passes to evolving gaming assets, dynamic NFTs are expanding what’s possible in the blockchain space. Whether you’re interested in exploring whether NFTs on Ethereum remain relevant or considering alternatives, understanding dynamic NFT technology is essential for anyone serious about Web3’s future.
Ready to dive in? Mint one on OpenSea, explore Chainlink documentation, or build your own dynamic NFT project. The future of NFTs is dynamic—don’t miss it.
External Resources: