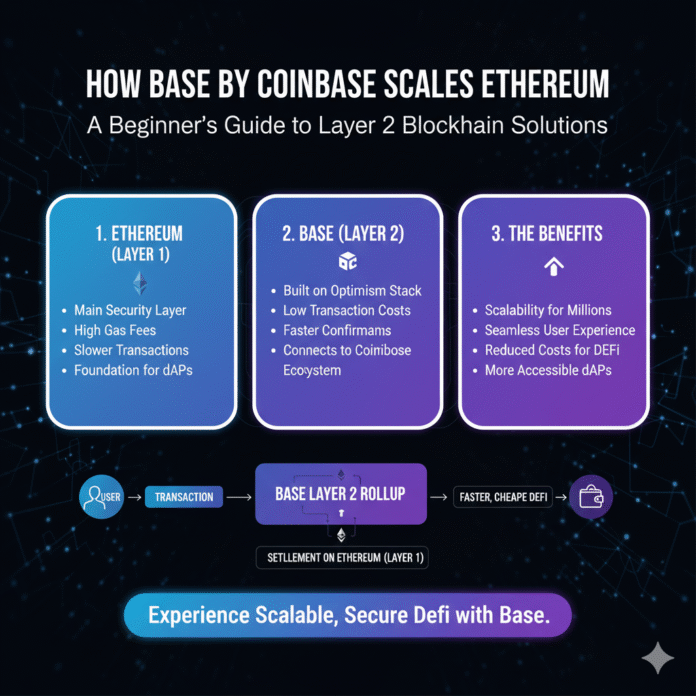
In the world of cryptocurrencies, Ethereum stands out as a powerhouse for decentralized applications, smart contracts, and digital assets. However, as its popularity has grown, so have its challenges—high transaction fees and slow processing times during peak usage. This is where scaling solutions come in, and one of the most prominent is Base, developed by Coinbase.
Base is an Ethereum Layer 2 network designed to make transactions faster and cheaper while maintaining the security of the main Ethereum blockchain. Coinbase launched it in 2023, with its public mainnet going live on August 9, 2023. Base has quickly become a key player in addressing Ethereum’s scalability issues. It helps onboard millions of new users into the crypto space.
This comprehensive guide explores how Base works to scale Ethereum. We’ll break down complex concepts into simple terms. We’ll use everyday examples to make it accessible for beginners. Whether you’re new to blockchain technology or curious about Layer 2 solutions, you’ll learn the fundamentals without getting lost in technical jargon. By the end, you’ll understand why Base is a game-changer for Ethereum’s future and the broader cryptocurrency ecosystem.
Why Does Ethereum Need Scaling Solutions?
Ethereum’s Core Functionality
Ethereum, often called the “world computer,” allows anyone to build and run applications without a central authority. It processes everything from simple token transfers to complex DeFi (decentralized finance) protocols. But with millions of users worldwide, the network can get congested. Think of it like a busy highway during rush hour.
Transactions pile up. This leads to high “gas fees”—the costs users pay to miners or validators to process them. Wait times can stretch from seconds to minutes or even hours.
The Technical Limitations
The root issue lies in Ethereum’s fundamental design. Every node in the network must verify and store every transaction to ensure security and decentralization. This architecture limits the blockchain to approximately 15-30 transactions per second (TPS). Global payment systems like Visa process thousands of TPS—far more than Ethereum currently handles.
Upgrades like the 2022 shift to Proof-of-Stake (The Merge) improved energy efficiency. However, they didn’t fully solve the scalability challenge. Developers needed a better solution.
Enter Layer 2 Solutions
To scale Ethereum without compromising its security or decentralization, developers turned to Layer 2 (L2) solutions. These are networks built on top of Ethereum (Layer 1 or L1). They handle most of the computational work off-chain while still leveraging Ethereum’s security guarantees.
Think of Ethereum as the main floor of a building: secure but crowded. L2 solutions like Base act as additional floors connected by elevators. They offload traffic while relying on the foundation’s strength. This approach keeps Ethereum decentralized and secure. At the same time, it dramatically boosts transaction speed and reduces costs for end users.
Base, in particular, uses a technology called optimistic rollups to achieve these improvements. This makes it significantly easier and more affordable for beginners to participate in the cryptocurrency ecosystem.
Learn more about Ethereum scaling: Optimism Documentation
Introducing Base: Coinbase’s Layer 2 Network
The Launch and Vision
Coinbase officially introduced Base on February 23, 2023. The platform started with a testnet environment for developers to experiment and build applications. Coinbase, one of the largest and most trusted cryptocurrency exchanges globally, incubated Base internally. The exchange leveraged its deep expertise in building user-friendly crypto products and services.
The primary goal behind Base’s creation was ambitious yet clear. Coinbase wanted to create a secure, low-cost, and developer-friendly platform for building onchain applications. The ultimate aim? To bring the next billion users into the cryptoeconomy and make blockchain technology accessible to mainstream audiences.
No Native Token Philosophy
Unlike some blockchain networks, Base has stated it has no plans for a native network token. Many other chains issue their own tokens for governance or fees. Base takes a different approach. The focus remains on building an open, inclusive ecosystem. The platform prioritizes accessibility and developer adoption over token economics.
Built on Proven Technology
Coinbase built Base in collaboration with Optimism. The platform leverages their open-source OP Stack technology. This technical foundation makes Base fully compatible with the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM). Developers can deploy existing Ethereum smart contracts to Base without needing to rewrite or modify their code. This represents a significant advantage for accelerating adoption.
Rapid Growth and Adoption
As of 2025, Base has experienced rapid growth. The platform now holds multi-billion-dollar total value locked (TVL). Some analyses ranked Base as number one by “ecosystem TVL” in 2025. However, by standard Layer 2 bridge metrics (TVS/TVL), Arbitrum remains the largest Layer 2 network.
The platform has achieved impressive transaction volumes. Base peaked around 10 million daily transactions in 2025. This demonstrates substantial real-world usage and adoption. For a detailed comparison of how Base stacks up against other leading L2s, check out our analysis of the Layer 2 wars between Arbitrum, Optimism, and Base.
Seamless Coinbase Integration
Coinbase seamlessly integrates Base with its platform. This allows easy onramps from traditional fiat currency to cryptocurrency. For beginners, this integration means you can transfer funds from your Coinbase wallet to Base with minimal friction. You’ll enjoy significantly lower fees for activities like NFT trading, DeFi lending, or token swaps.
Cross-Chain Considerations
Base isn’t natively interoperable with other blockchain networks like Solana. Third-party bridge protocols achieve cross-chain interoperability with Solana and other chains. These include Wormhole and Chainlink CCIP. Base doesn’t provide this as a built-in feature.
Official resources:
The Core Technology: Optimistic Rollups Explained
What Are Optimistic Rollups?
At the heart of how Base scales Ethereum is a technology called optimistic rollups. This is a specific type of Layer 2 scaling solution. To understand this concept, think of rollups as a bundling service.
Instead of sending individual packages (transactions) through the mail system (Ethereum mainnet) one at a time, you pack many transactions into one large box. Then you ship it once. This saves both time and money for everyone involved.
Why “Optimistic”?
Optimistic rollups earn their name because they operate on an “optimistic” assumption. They assume all transactions are valid by default. They don’t check each one upfront through complex cryptographic proofs.
This approach contrasts with zero-knowledge (ZK) rollups. ZK rollups immediately prove validity using sophisticated mathematical computations. In optimistic systems, the network processes transactions off-chain on the Layer 2 network. Then it batches them together. Finally, it submits them to Ethereum Layer 1 as a single consolidated “rollup” transaction.
How Optimistic Rollups Work: A Simple Breakdown
Off-Chain Execution: Users send their transactions to Base’s network. The network executes them quickly and at low cost. This doesn’t congest the main Ethereum blockchain.
Batching Process: A component called the sequencer collects and orders these transactions into organized batches. This ensures proper transaction ordering. It also prevents issues like front-running.
Data Posting: The network compresses the batch and posts it to Ethereum Layer 1 as calldata. This ensures data availability. Anyone can verify the transactions if needed.
Challenge Period: After posting, there’s a challenge window. The OP-Stack rollups currently set this at approximately seven days. During this time, anyone can submit fraud proofs if they detect invalid transactions. This security mechanism ensures system integrity.
Settlement on Layer 1: Once the challenge period passes without disputes, the network finalizes the state updates. It settles them on Ethereum. They inherit its robust security guarantees.
The Benefits of This Approach
This methodology dramatically reduces the computational load on Ethereum. It handles transaction execution off-chain. At the same time, it still uses Layer 1 for security, data availability, and final settlement.
Base’s use of the OP Stack ensures Ethereum-grade security. The platform includes additional features like shared upgrades across the Superchain ecosystem. Anyone can audit the fully open-source code.
A Practical Analogy
For a practical analogy, imagine buying coffee. On Ethereum Layer 1, each purchase is like paying a high toll on a congested bridge for every transaction. On Base, multiple coffee purchases from many customers get grouped together. Only one toll gets paid for the entire group. This makes each individual cup significantly cheaper while maintaining the same security guarantees.
Technical documentation: Optimism Docs
Step-by-Step: How Base Processes Transactions
Transaction Initiation
To see how Base scales Ethereum in action, let’s walk through a typical transaction flow. We’ll examine each stage of the process from start to finish.
First, a user initiates a transaction on Base. For example, they might swap ETH for a stablecoin in a decentralized finance (DeFi) application. On Base, users pay gas fees in ETH, just like on Ethereum mainnet. However, the fees are usually much lower—often 10 to 100 times cheaper than Layer 1.
This dramatic cost reduction occurs for a specific reason. Only compressed transaction data (not full computational execution) needs posting to the Ethereum mainnet.
Sequencing and Batching
The sequencer collects incoming transactions. Coinbase currently operates this centralized but progressively decentralizing component. The sequencer orders transactions to prevent manipulation issues like front-running. Then it creates organized batches.
Each batch includes the transaction data and a new state root. Think of the state root as a cryptographic snapshot. It captures the network’s updated state after processing all transactions in the batch.
Submission to Ethereum Layer 1
Next, the system submits the completed batch to Ethereum Layer 1. Base separates execution (which happens on Layer 2) from settlement and data availability (which happen on Layer 1). This ensures complete transparency and verifiability.
The system posts the transaction data as calldata. This is a relatively inexpensive way to store data on Ethereum. It keeps the data accessible to anyone who wants to verify the transactions.
Challenge Period and Fraud Proofs
During the challenge period, verifiers can check the batch for validity. Anyone running a node and monitoring the network can do this. If someone detects fraud, such as an invalid signature or incorrect state transition, they can submit a fraud proof to the Ethereum mainnet.
If the fraud proof proves valid, the network rejects the faulty batch. The sequencer may face penalties. This economic incentive structure keeps the system honest and secure.
Finality and Withdrawals
Transaction finality occurs after the challenge window expires without disputes. For users withdrawing funds from Base back to Ethereum Layer 1, this typically means waiting approximately seven days for complete on-chain security.
Third-party liquidity providers and bridges offer fast exit services. These can shorten the user experience. However, they don’t change the underlying on-chain finality window required for maximum security.
Gas Fees and Security
The network calculates gas fees on Base dynamically. It bases them on Layer 2 network activity. However, fees remain consistently lower than Layer 1. The security model derives from Ethereum’s validators. Coinbase’s industry-leading security best practices and infrastructure supplement this.
Developer resources:
Benefits for Users and Developers
User Benefits
Base’s innovative scaling approach delivers clear, tangible advantages. Both end users and application developers benefit. This makes it an attractive platform for building and using blockchain applications.
Lower Transaction Costs: Transactions on Base cost dramatically less than on Ethereum mainnet. They often cost just a few cents instead of tens of dollars. This makes crypto accessible for everyday use cases like micro-payments, gaming, or social media tipping.
Faster Transactions: Base processes transactions near-instantly. Confirmation times measure in seconds rather than minutes or hours. This provides a user experience comparable to traditional web applications.
Easy Onboarding: Integration with Coinbase means seamless fiat-to-crypto onramps. This reduces technical barriers for beginners. Many newcomers feel intimidated by more complex blockchain interactions. For a comprehensive overview of Base’s features and advantages, explore our complete guide to Base by Coinbase.
Ethereum Security: Despite operating off-chain, Base inherits Ethereum’s battle-tested security guarantees. This gives users confidence in the safety of their funds and transactions.
Developer Benefits
EVM Equivalence: Full compatibility with the Ethereum Virtual Machine means developers can deploy existing smart contracts without modifications. This significantly reduces development time and costs.
Developer Tools: Base provides modern development tools. These include account abstraction for gasless transactions. This makes it easier to create user-friendly applications. Users don’t need to hold ETH for gas.
Innovation Enablement: Lower costs and higher throughput enable new categories of applications. These were previously uneconomical on Layer 1. Examples include social networks, gaming platforms, and complex DeFi protocols.
Network Effects: Building on Base provides access to Coinbase’s massive user base and ecosystem. This offers built-in distribution advantages for new applications.
Network-Wide Impact
Beyond individual benefits, Base helps reduce congestion on the Ethereum mainnet. This lowers fees network-wide. It benefits all Ethereum users. The platform can handle thousands of transactions per second. Compare this to Ethereum’s 15-30 TPS. This dramatically expands the blockchain’s practical capacity.
Industry analysis: The Block
The Growing Ecosystem and Adoption
Ecosystem Support and Partnerships
Base has rapidly developed a thriving ecosystem. The platform includes applications, protocols, and partnerships. These demonstrate real-world adoption and utility.
Base launched the Base Ecosystem Fund to support early-stage projects. The fund provides financial resources and technical guidance to promising teams. The network has attracted partnerships with major DeFi protocols like Uniswap. It also partners with identity projects like Worldcoin. Numerous NFT marketplaces and gaming platforms have joined the ecosystem.
The Superchain Vision
Base is a core component of the “Superchain” vision. This is an ambitious plan to create an interconnected network of OP Stack chains. These chains share security, liquidity, and development resources. This approach allows different Layer 2 networks to interoperate seamlessly. It creates a more unified and efficient blockchain ecosystem rather than fragmented, isolated networks.
Adoption Metrics and Growth
By 2025, Base hosts hundreds of popular decentralized applications. These span categories including DeFi, NFTs, gaming, and social media. The platform has achieved multi-billion-dollar total value locked.
Different measurement methodologies yield different rankings. On L2BEAT’s standard Layer 2 metrics measuring value secured through bridges (TVS/TVL), Arbitrum still leads. However, separate “ecosystem TVL” rankings include different categories of locked value. These have at times placed Base first in 2025.
Transaction volumes have surged dramatically. The network processes approximately 10 million daily transactions during peak periods in 2025. This demonstrates substantial real-world usage beyond speculation. This transaction throughput represents a significant achievement. It makes blockchain technology practical for mainstream applications.
Ecosystem tracking:
The Future of Base and Ethereum Scaling
Decentralization Roadmap
Base has ambitious plans for continued development and progressive decentralization. The platform positions itself as a cornerstone of Ethereum’s scaling roadmap.
Base works toward progressive decentralization through a multi-stage process. Coinbase originally targeted achieving “Stage 2” decentralization in 2024. However, Base achieved “Stage 1” in April 2025 according to L2BEAT’s classification framework.
Stage 2 decentralization involves additional security councils, fraud proof maturity, and further decentralization of critical components. As of October 18, 2025, Base hasn’t yet achieved this stage. However, it remains a key development priority.
Ethereum Protocol Upgrades
As Ethereum continues to evolve with planned upgrades like Danksharding (also called proto-danksharding or EIP-4844), Base will integrate these improvements. This will achieve even better data availability and lower costs.
These Ethereum mainnet upgrades will directly benefit all Layer 2 solutions, including Base. They will reduce the cost of posting data to Layer 1. They will also increase overall system capacity.
Cross-Chain Future
Base doesn’t natively support cross-chain functionality with networks like Solana. However, the ecosystem continues to improve through third-party bridge protocols. These include Wormhole and Chainlink CCIP.
Users seeking cross-chain activity should rely on these established bridge solutions. Don’t assume native support exists. Carefully evaluate bridge security before transferring significant value.
Scaling to Billions
Base’s ultimate vision extends beyond technical improvements. It aims to fundamentally change how people interact with blockchain technology. By combining accessibility, low costs, and robust security, the platform aims to become a primary gateway. It wants to help billions of users enter the cryptoeconomy. The goal is to make blockchain technology as accessible and user-friendly as today’s mobile applications.
Bridge resources: Wormhole
Conclusion: Base as Ethereum’s Scaling Gateway
Base by Coinbase is revolutionizing Ethereum scaling through its implementation of optimistic rollups. It offers a secure, efficient, and accessible alternative to Layer 1’s inherent limitations. The platform processes transactions off-chain. At the same time, it leverages Ethereum’s security for final settlement. This makes cryptocurrency more inclusive and practical for everyday use.
For beginners entering the blockchain space, Base represents a gateway to affordable onchain experiences. You won’t face the intimidating gas fees and slow confirmation times of Ethereum mainnet. For developers and experts, it provides a scalable foundation for innovation. It enables new categories of applications. These were previously uneconomical or impractical on Layer 1.
When you need cross-chain activity—for example, bridging assets to networks like Solana—rely on established third-party bridge protocols. Use services like Wormhole or Chainlink CCIP. Don’t assume native support exists. Always research bridge security carefully before moving significant value between chains.
As Ethereum continues its evolution toward becoming a truly global settlement layer, Base stands positioned as one of the most important scaling solutions. It combines Coinbase’s user experience expertise, Optimism’s battle-tested technology, and Ethereum’s unmatched security. Together, these bring blockchain technology to the masses.
Key Resources and External Links:
- Base Official Website
- Base Documentation
- Coinbase
- Optimism Documentation
- L2BEAT Layer 2 Analytics
- The Block
- The Defiant
- Wormhole Bridge
- Forbes Blockchain Coverage
This guide is for educational purposes only and does not constitute financial advice. Always conduct your own research before interacting with blockchain protocols or investing in cryptocurrency.