In the fast-evolving world of blockchain technology, scalability has long been a major hurdle. As more people adopt cryptocurrencies and decentralized applications (dApps), networks like Ethereum often face congestion, leading to high fees and slow transaction times. Layer 2 solutions have helped alleviate these issues, but now Layer 3 is emerging as the next step forward. This article explores what Layer 3 means for everyday users, breaking down complex concepts into simple terms. Whether you’re a beginner dipping your toes into crypto or a seasoned enthusiast, understanding Layer 3 can help you grasp how blockchain is becoming more efficient, affordable, and user-friendly.
Layer 3 blockchains build on existing infrastructure to create specialized environments tailored for specific applications. They’re not replacing Layer 1 or Layer 2 but enhancing them, promising lower costs, faster speeds, and better interoperability. As we head into 2025, with predictions from sources like Equilibrium Labs of over 2,000 Layer 2 and Layer 3 solutions in the Ethereum ecosystem, this technology is poised to transform how users interact with Web3.
Let’s dive in.
Understanding Blockchain Layers: A Simple Breakdown
To appreciate Layer 3, it’s essential to start with the basics of blockchain layers. Think of blockchain as a multi-story building: each floor serves a unique purpose, but they all work together to support the structure.
Layer 1: The Foundation
Layer 1 (L1) is the ground floor—the base blockchain network where everything starts. Examples include Ethereum, Bitcoin, Solana, and Binance Smart Chain. These handle core functions like transaction validation, consensus (how the network agrees on data), and security. L1s are decentralized and secure but often struggle with scalability. For instance, during peak times, Ethereum’s transaction fees can skyrocket, making simple transfers expensive for average users.
L1s prioritize decentralization and security over speed, which is why they can process only a limited number of transactions per second (TPS). According to industry data, Bitcoin processes roughly 3–7 TPS, and Ethereum typically handles approximately 15–30 TPS. This limitation has driven the need for upper layers.
Layer 2: The Scaling Solution
Layer 2 (L2) sits on top of L1, acting like an extension to boost performance without altering the base layer. L2s process transactions off the main chain and bundle them before settling back on L1, reducing congestion. Popular L2s include Arbitrum, Optimism, and Polygon on Ethereum, or Lightning Network on Bitcoin.
For users, L2s mean cheaper and faster transactions. A transfer that might cost $10 on Ethereum L1 could drop to pennies on an L2 like Arbitrum. They use techniques like rollups—optimistic rollups (assuming transactions are valid unless challenged) or zero-knowledge (ZK) rollups (proving validity mathematically)—to achieve this. After Ethereum’s Dencun upgrade (EIP-4844) in March 2024, many L2s reported fee reductions by approximately 10x or more, as the introduction of blob transactions made L2 data significantly cheaper.
However, L2s are general-purpose, handling multiple dApps, which can still lead to some bottlenecks in highly specialized scenarios.
Introducing Layer 3: The Application Layer
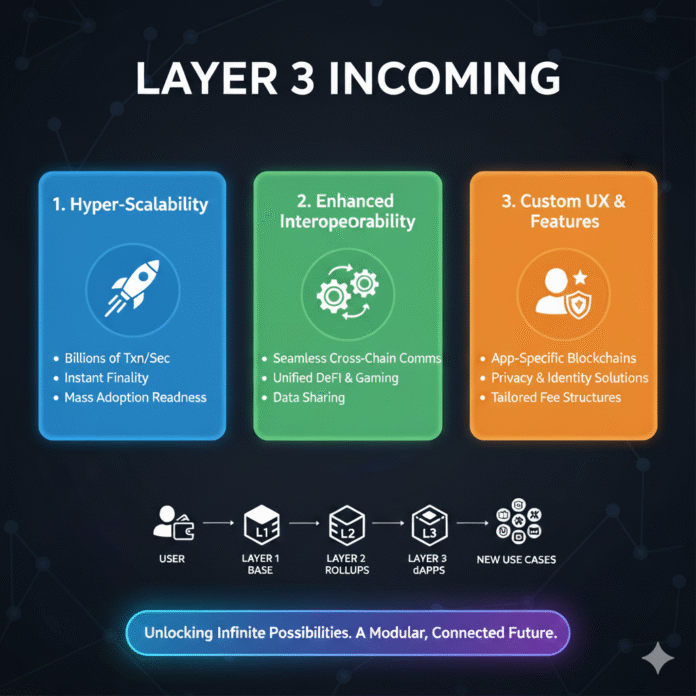
Layer 3 (L3) is the top floor, built atop L2 to provide even more targeted improvements. Often called the “application layer,” L3 focuses on creating customizable, app-specific chains. These aren’t general networks but tailored environments for particular uses, like gaming or decentralized finance (DeFi).
Unlike L2s, which scale broadly, L3s optimize for specific needs, such as privacy, high-speed microtransactions, or interoperability across chains. As Vitalik Buterin has noted, L3s make most sense for specialized functions like privacy, customized scaling, and validiums, rather than simply providing “more of the same” scaling already accomplished by L2s.
They inherit security from L1 and L2 while adding flexibility. For example, an L3 might allow developers to adjust gas fees or governance rules without affecting the underlying layers. This makes blockchain more accessible, turning complex tech into seamless experiences for users.
How Layer 3 Works: A Step-by-Step Explanation
Layer 3 operates by leveraging L2 as its settlement layer, much like L2 uses L1. Here’s a simplified process:
Transaction Execution: Users interact with a dApp on the L3 chain. Transactions happen here, optimized for the app’s needs (e.g., rapid in-game purchases).
Batching and Proofs: L3 bundles transactions and generates a proof (using ZK technology or similar) to verify their validity.
Settlement on L2: The proof is sent to the L2 for verification. Many L3 frameworks, such as Arbitrum Orbit, support settling to an L2, which then posts compressed data to L1.
Final Confirmation: L1 records the settlement, ensuring security without handling every detail.
This “fractal scaling” approach allows for data compression and cost reduction. StarkWare introduced the L3 fractal scaling concept specifically to enable app-specific hyper-scalability and privacy on top of L2s. In practice, L3s can run as validiums (proofs with off-chain data availability via committees) or as full rollups—trading off cost versus security.
This setup shields users from network congestion, providing stable performance even during high-traffic periods.
Benefits of Layer 3 for Users: Making Blockchain Practical
Layer 3 isn’t just technical jargon—it’s about real improvements that make blockchain usable for everyone. Here are the key advantages:
Lower Transaction Costs: By settling on L2 and adding compression, L3s can reduce fees to fractions of a cent. Evidence from post-Dencun implementations shows multiple L2s and L3s reporting 10x–100x lower costs, with some achieving sub-cent fees.
Faster Speeds: L3s handle high-throughput needs, enabling near-instant transactions for specialized applications.
Enhanced Privacy: Some L3s incorporate zero-knowledge proofs or encryption layers, protecting user data and transaction details.
Better Interoperability: Some L3 technology stacks aim to streamline cross-chain flows, such as zkSync’s ZK Stack chains (formerly called hyperchains), which enable composable ecosystems.
Customized Experiences: Tailored for specific applications, L3s can simplify user experience while exposing advanced features for power users who need them.
Scalability Without Compromise: Users get L1 security with L2 speed and L3 customization, enabling complex applications from gaming to real-world asset tokenization.
Real-World Examples of Layer 3 Projects
Several L3 projects are already making waves, demonstrating practical value:
Arbitrum Orbit: Built on Arbitrum (an Ethereum L2), Orbit lets developers create custom L2 or L3 chains that can settle to Arbitrum and ultimately Ethereum.
zkSync ZK Stack: A developer framework for sovereign ZK chains that can be composed into ecosystems, often described as “L3” when stacked over an L2. Learn more at zkSync documentation.
Orbs Network: Positions itself as a Layer-3 infrastructure on top of EVM chains (Ethereum, BNB Chain, Polygon, Avalanche), adding decentralized backend services for DeFi automation. Visit Orbs documentation.
Xai (XAI) Games: An L3 on Arbitrum designed specifically for gaming throughput and low-cost NFT transactions, addressing the unique needs of blockchain gaming.
Degen Chain: An L3 built with Arbitrum Orbit that settles to Base, powering the DEGEN ecosystem with applications like DegenSwap.
Dojo on Starknet: A game-engine and toolchain enabling real-time, on-chain games atop Starknet, used by numerous Starknet gaming projects. More information at Dojo Engine.
Challenges and Considerations with Layer 3
While promising, Layer 3 isn’t without hurdles. Security is inherited from lower layers, so vulnerabilities in L1 or L2 could potentially affect L3s. Finding validators and sequencers for new chains can be challenging, potentially leading to centralization risks. Validiums specifically introduce a data-availability trust assumption through Data Availability Committees (DACs), trading some decentralization for lower costs.
For users, this means choosing reputable projects and understanding trade-offs—such as accepting slightly lower security guarantees for significantly cheaper fees. As the technology matures, these issues are being addressed through better protocols, improved infrastructure, and community governance mechanisms.
The Future of Layer 3: Developments in 2025 and Beyond
Looking ahead, 2025 is set to be a breakout year for Layer 3 adoption. Some industry predictions forecast that Ethereum’s “scaling factor” (combined L2/L3 TPS versus L1) could exceed 200× as new chains launch and existing ones scale further. Projects on Starknet are also exploring “hyperscaling” patterns, such as Integrity Verifier mechanisms, to multiply throughput across app-specific technology stacks.
Emerging trends include integration with artificial intelligence, GameFi 2.0 developments, and real-world asset tokenization. However, Vitalik Buterin has cautioned against unnecessary complexity, noting that L3s shine brightest in specialized roles—such as privacy enhancements, customized scaling solutions, and validium implementations—rather than simply duplicating what L2s already accomplish.
Conclusion: Embracing Layer 3 for a Better Web3 Experience
Layer 3 represents the next evolution in blockchain technology, building on L1 and L2 foundations to deliver tailored, efficient solutions for specific use cases. For users, it means cheaper, faster, and potentially more private interactions, opening doors to innovative applications in gaming, DeFi, supply chain management, and beyond. As 2025 unfolds, staying informed about projects like Arbitrum Orbit, zkSync ZK Stack, and Orbs Network will help you navigate this rapidly evolving space.
While challenges remain around security assumptions, decentralization, and ecosystem maturity, the benefits are compelling, making blockchain technology more approachable for beginners and more powerful for experienced users. If you’re exploring crypto and Web3, consider starting with an L2 wallet and experimenting with emerging L3 dApps—the future of decentralized technology is here, and it’s increasingly user-centric.
For more information on blockchain scaling solutions, compare different approaches in our Layer 2 wars analysis, learn about Optimism’s scaling approach, or explore our comprehensive guide to Ethereum Layer 2 solutions. You can also visit Ethereum.org, L2BEAT for Layer 2 analytics, and follow developments from key projects like Arbitrum, StarkWare, and zkSync.Retry