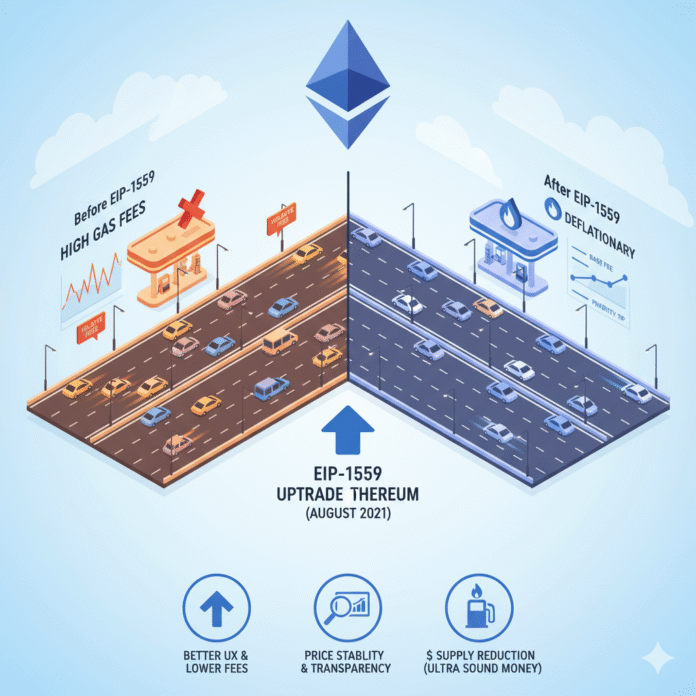
Introduction: From Fee Chaos to Algorithmic Pricing
Before mid-2021, using Ethereum often felt like surge-pricing roulette. Transaction fees were set via a first-price auction: you guessed a gas price, hoped it was enough, and either overpaid or got stuck in the mempool waiting indefinitely. However, on August 5, 2021, the London upgrade activated EIP-1559, replacing that unpredictable auction with an algorithmic base fee that gets burned—permanently removing ETH from circulation every block.
As a result, the network now offers far more predictable fees and a structural scarcity engine tied to network usage. Furthermore, that predictability dramatically improves user experience, while the burn mechanism can—under the right conditions—support ETH’s long-term investment value.
Reality check: Nevertheless, EIP-1559 was not designed to “make gas cheap.” Instead, it smooths and clarifies pricing. Actual transaction costs still depend on network demand and capacity—learn more about how Ethereum gas fees work in our beginner’s guide.
Understanding How Ethereum Fees Work Today
The Three Components of EIP-1559 Transaction Fees
EIP-1559 split transaction fees into three distinct components. First, there’s a base fee set by the protocol that adjusts each block and is burned. Second, there’s a priority fee (tip) that’s optional extra to jump the queue and paid to validators. Finally, there’s a max fee as your absolute ceiling. Consequently, modern Ethereum wallets like MetaMask and Rainbow automatically estimate these values for you.
Two Critical Design Features That Make Fees Predictable
1. Elastic blocks for demand absorption: Importantly, blocks target approximately 50% fullness and can temporarily expand up to 2× the target size to absorb demand bursts. Therefore, this flexibility reduces panic bidding during network congestion.
2. Bounded fee changes prevent price whiplash: Moreover, the base fee can move by at most ±12.5% per block (denominator = 8), limiting extreme price whiplash. As a result, this makes fee prediction far more reliable than the old auction model.
What EIP-1559 Actually Fixed
Problem #1: Pricing Clarity Reduces Overpayment
Previously, the old first-price auction pushed users to overbid or wait. In contrast, EIP-1559 replaces it with a protocol-quoted reserve price (the base fee) and a small tip market. Thus, it improves predictability and reduces typical overpayment. Although you still pay for scarce block space, you’re no longer guessing in the dark.
Problem #2: Monetary Policy Through Fee Burning
Additionally, burning the base fee permanently reduces ETH supply relative to a world where all fees go to proposers. While this doesn’t guarantee price appreciation, it nonetheless adds a usage-linked scarcity channel to Ethereum’s tokenomics—similar to corporate stock buybacks. For investors comparing different blockchain assets, understanding these tokenomics differences between Bitcoin and Ethereum becomes crucial.
What EIP-1559 Did Not Fix
On the other hand, it does not magically lower L1 fees. Indeed, gas price is still set by demand versus capacity. Specifically, EIP-1559 mostly improves fee estimation and volatility, not the underlying cost of block space. Instead, true scaling improvements come from Layer 2 solutions and protocol upgrades like sharding.
The Evolution: 2022–2025 Major Network Upgrades
The Merge (September 15, 2022): Proof-of-Stake Transition
Subsequently, Ethereum moved to proof-of-stake, slashing energy use by approximately 99.95% and cutting ETH issuance by roughly 90%. Consequently, this amplifies the relative impact of fee burns. Notably, base fees still burn exactly as before—only now validators replace miners as block proposers.
Learn more about Ethereum’s proof-of-stake consensus on the official Ethereum website.
Dencun Upgrade (March 13, 2024): The Layer 2 Revolution
Later, the Dencun upgrade activated EIP-4844 (proto-danksharding), adding cheap “blob” data storage for rollups. Consequently, Layer 2 fees collapsed, often to cents, while L1 fees remained demand-driven. However, there’s a trade-off: cheaper fees can reduce burn, occasionally nudging ETH supply inflationary again.
Real-World Impact on Transaction Costs
Concrete impact: After Dencun, L2s like Optimism and Base routinely priced transactions at pennies. Meanwhile, popular Layer 2 networks include:
- Arbitrum – One of the largest rollups by TVL
- Optimism – Pioneer in optimistic rollup technology
- Base – Coinbase’s leading Layer 2 solution
- zkSync – Leading zero-knowledge rollup
Furthermore, by March 13, 2025, average gas price dropped from approximately 72 gwei (2024) to around 2.7 gwei. Nevertheless, that reflects demand cycles plus scaling effects—not EIP-1559 alone.
Investor Perspective: When Does the Burn Mechanism Help?
Total ETH Burned: The Numbers Tell a Story
Since the London upgrade in August 2021, the network has burned over 5.3 million ETH as of October 2025. Clearly, that’s a massive, usage-linked supply sink. Additionally, you can track real-time burn data at ultrasound.money or beaconcha.in.
For a comprehensive look at how this burn rate affects Ethereum’s overall metrics, check out our detailed statistical analysis of Ethereum’s key numbers.
Understanding Net Supply Dynamics: Deflation vs. Inflation
Importantly, post-Merge issuance dropped sharply. Therefore, when network activity and fees are high, burn exceeds issuance, creating net deflation. However, after Dencun lowered fees, burn slowed and ETH briefly turned inflationary in 2024. Thus, the deflationary effect is state-dependent, not permanent.
Investment Implications: The Bottom Line
Ultimately, EIP-1559 tightens ETH economics by converting network activity into burn. Consequently, that can support price over long horizons, especially alongside lower issuance. Nevertheless, it’s not automatic: if fees fall (great for users!), burn falls (less supply contraction). Therefore, the long-term investment thesis relies on sustained usage growth across L1 and L2 and continued execution of the scaling roadmap.
For deeper analysis, check Ethereum’s official roadmap.
For Beginners: Understanding EIP-1559 Through a Simple Analogy
To illustrate, before EIP-1559, Ethereum was a crowded highway with auction-style toll booths—everyone shouting prices. In contrast, with EIP-1559, the protocol posts a clear toll (base fee) that adjusts gradually with traffic. Moreover, you can add a tip to pass sooner. Meanwhile, the posted toll gets shredded (burned) instead of going to the operator—making “tickets” (ETH) a bit scarcer over time.
2025 Reality Checks: Key Facts and Figures
Timeline and Technical Specifications
First and foremost, EIP-1559 went live August 5, 2021 with the London upgrade. Specifically, the design includes elastic blocks up to 2× target size and ±12.5% per-block base-fee adjustment. Furthermore, the base fee is burned, while tips go to the proposer.
Historical Fee Comparison
Notably, peak fee pain before EIP-1559 saw average L1 transaction fees top $60 in May 2021 during surging DeFi demand. In contrast, post-Dencun, L2 fees dropped approximately 10× or more. As a result, many L2 transfers now cost just cents.
Does EIP-1559 Make Ethereum “Cheaper and More Profitable”?
Analyzing Cost Reduction Claims
Cheaper in Practice?
On one hand, EIP-1559 reduces overpayment and fee volatility and enables wallets to set fees sensibly. However, true “cheap” transactions come mainly from scaling upgrades like EIP-4844 and demand cycles.
More Profitable: The Investment Thesis
On the other hand, the burn ties ETH scarcity to network usage. Combined with lower issuance post-Merge, it can support value over time—if activity stays strong. Nevertheless, when fees are very low, burn slows and supply can expand slightly. Therefore, it’s a conditional tailwind, not a guarantee. Investors interested in alternative smart contract platforms may also want to explore how BNB’s tokenomics compare to Ethereum’s model.
Key Takeaways: EIP-1559 in Plain English
- EIP-1559 equals predictable fees plus burn mechanism: Primarily, it fixes user experience more than it slashes L1 costs.
- Scaling drives fee reduction: Specifically, Layer 2 solutions plus EIP-4844 are why 2024–2025 fees feel dramatically lower.
- Millions of ETH burned: Notably, the burn has destroyed millions of ETH since 2021. However, whether net supply shrinks depends on activity versus issuance.
Additional Resources for Learning More
To further expand your knowledge:
- Ethereum Foundation Blog – Official announcements and technical updates
- EIP-1559 Full Specification – Complete technical details
- Etherscan Gas Tracker – Real-time gas price monitoring
- L2Beat – Layer 2 scaling solution comparison
- CoinDesk Ethereum Coverage – Latest news and analysis
- Investopedia Ethereum Guide – Educational resources
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and does not constitute financial advice. Cryptocurrency investments carry significant risk. Always conduct your own research and consult with financial professionals before making investment decisions.